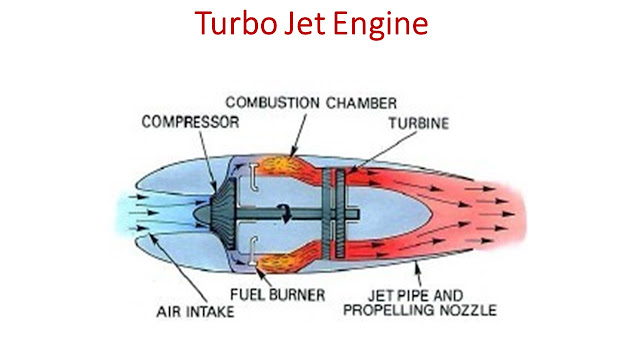
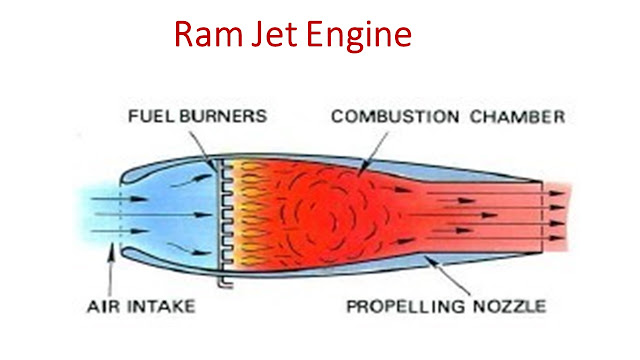
1. Aircraft Structures
-
Fuselage provides strength, rigidity, and safe enclosure for crew, passengers, and cargo.
-
Semi-monocoque fuselage construction uses frames, stringers, bulkheads, and skin for strength.
-
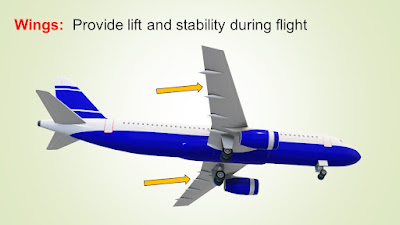
Wing structure contains spars, ribs, and stringers to maintain aerodynamic shape.
-
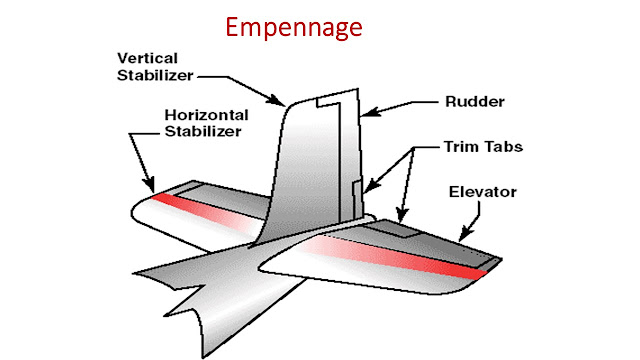
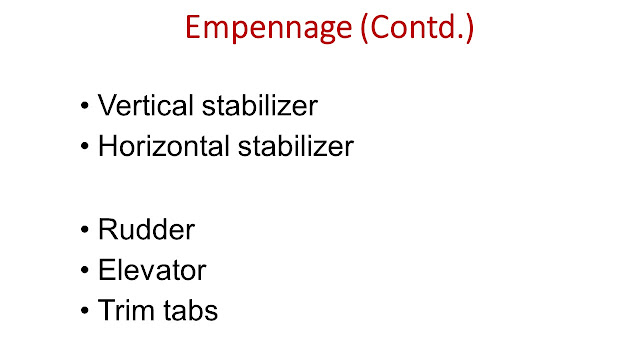
Empennage includes horizontal stabilizer, vertical stabilizer, rudder, and elevator.
-
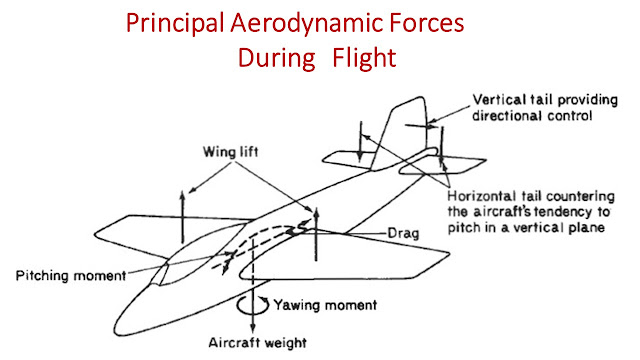
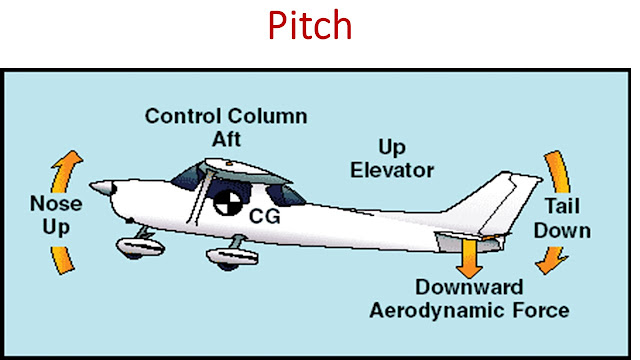
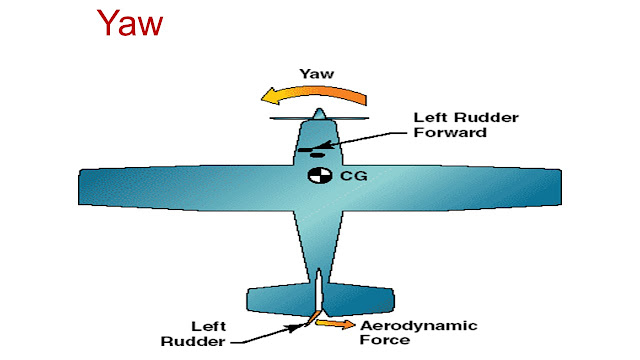
Primary flight controls are ailerons, elevator, and rudder for maneuvering.
-
Secondary flight controls include flaps, slats, spoilers, and trim tabs.
-
Landing gear absorbs landing loads, provides taxi support, and ground clearance.
-
Hydraulic actuators extend and retract landing gear during operation.
-
Aircraft doors use locking mechanisms to withstand cabin pressurization loads.
-
Composite materials reduce weight, improve corrosion resistance, and increase strength.
2. Hydraulic Systems
-
Hydraulic system uses pressurized fluid to transmit force and motion.
-
Pascal’s law states pressure applied to fluid is transmitted equally.
-
Hydraulic reservoirs store fluid, maintain pressure, and remove air bubbles.
-
Hydraulic pumps convert mechanical energy into fluid power pressure.
-
Filters remove contaminants, dirt, and particles from hydraulic system.
-
Hydraulic accumulators store pressure, absorb shocks, and damp pulsations.
-
Actuators convert hydraulic pressure into mechanical linear or rotary motion.
-
Pressure relief valves prevent over-pressurization and system damage.
-
Hydraulic lines are color-coded and labeled for maintenance safety.
-
Skydrol hydraulic fluid is fire resistant but corrosive to skin.
3. Pneumatic Systems
-
Pneumatic systems use compressed air for brakes, engine starting, and de-icing.
-
Sources of pneumatic power include engine bleed air and APU.
-
Pressure regulators maintain required pneumatic pressure during operation.
-
Moisture separators remove water vapor to avoid icing problems.
-
Pneumatic accumulators stabilize system pressure fluctuations effectively.
-
Over-pressure relief valves protect pneumatic system against excessive pressure.
-
Pneumatic system operates wing anti-ice boots using compressed air.
-
Engine cross-bleed valve controls pneumatic supply between engines.
-
Pneumatic leak detection uses overheat sensing loops along ducts.
-
Pneumatic manifolds distribute bleed air to multiple aircraft systems.
4. Landing Gear Systems
-
Retractable landing gear reduces drag and improves aerodynamic performance.
-
Nose gear provides steering control during taxiing and take-off.
-
Main gear supports aircraft weight during landing and ground operations.
-
Oleo strut absorbs landing shocks using hydraulic oil and nitrogen.
-
Landing gear doors reduce drag and protect retracted gear.
-
Anti-skid system prevents wheel lock-up and reduces tire wear.
-
Brake units are multi-disc or carbon disc assemblies for stopping.
-
Emergency extension system uses free-fall, pneumatic, or manual methods.
-
Proximity sensors provide landing gear position indication to cockpit.
-
Tire pressure must be checked regularly for safety and performance.
5. Electrical Systems
-
Aircraft electrical system provides power to avionics, lights, and instruments.
-
Direct Current (DC) is supplied by batteries and DC generators.
-
Alternating Current (AC) is supplied by alternators and inverters.
-
Transformer rectifier units convert AC power into regulated DC.
-
Circuit breakers protect wiring and components from overcurrent.
-
Bus bars distribute electrical power to aircraft subsystems.
-
Static inverters convert DC battery power into AC emergency power.
-
Ground power unit supplies external electrical power during maintenance.
-
Auxiliary Power Unit provides electrical and pneumatic power on ground.
-
Emergency power is supplied by battery when generators fail.
6. Avionics Systems
-
Pitot-static system measures airspeed, altitude, and vertical speed.
-
Altimeter displays aircraft altitude above mean sea level.
-
Airspeed indicator uses dynamic and static pressure difference.
-
Vertical speed indicator shows climb or descent rate.
-
Attitude indicator provides artificial horizon using gyroscopes.
-
Heading indicator gives aircraft directional reference during flight.
-
Radio altimeter measures height above ground using radio waves.
-
Flight Management System integrates navigation, performance, and guidance.
-
GPS provides global navigation signals using satellites.
-
Autopilot reduces pilot workload by automatically controlling flight path.
7. Fuel Systems
-
Fuel tanks store fuel inside wings, fuselage, or stabilizers.
-
Boost pumps deliver pressurized fuel to engines and APU.
-
Cross-feed valves allow fuel transfer between tanks during flight.
-
Fuel control unit meters correct amount of fuel to engine.
-
Fuel jettison system allows safe fuel dumping during emergencies.
-
Fuel filters remove water, contaminants, and particles from fuel.
-
Fuel quantity is measured by capacitance probes inside tanks.
-
Vent system prevents vacuum formation inside fuel tanks.
-
Fuel heaters prevent ice formation inside fuel lines.
-
Gravity feed ensures emergency fuel supply if pumps fail.
8. Environmental Systems
-
Pressurization system maintains cabin altitude and passenger comfort.
-
Outflow valve regulates cabin pressure by controlling air discharge.
-
Safety valve prevents excessive over-pressurization or negative pressure.
-
Air conditioning packs provide conditioned air using bleed air.
-
Mixing unit blends hot bleed air with cold conditioned air.
-
Recirculation fans reduce bleed air demand and save fuel.
-
Cabin temperature is controlled automatically or manually by pilots.
-
Oxygen system supplies crew and passengers during depressurization.
-
Chemical oxygen generators supply passenger masks during emergencies.
-
Portable oxygen bottles are available for crew mobility.
9. Fire Protection Systems
-
Fire detection uses continuous-loop, spot, and flame detectors.
-
Smoke detectors are installed in cargo compartments and lavatories.
-
Fire bottles contain Halon extinguishing agent under pressure.
-
Squibs rupture fire bottles for agent discharge when activated.
-
Engine fire handle closes fuel, hydraulic, and bleed air valves.
-
APU fire extinguishing system is independent from engine system.
-
Cargo fire suppression system uses multiple Halon bottles sequentially.
-
Fire warning indications are displayed on cockpit annunciator panels.
-
Built-in test equipment checks fire detection circuits automatically.
-
Cabin crew training includes fire drill and extinguisher operation.
10. Ice and Rain Protection
-
Pneumatic boots break ice by inflation and deflation cycles.
-
Thermal anti-ice uses hot engine bleed air on wings.
-
Windshield heat prevents ice formation and removes fogging.
-
Pitot probes use electrical heating for anti-ice protection.
-
Propeller de-icing uses electrical heating elements on blades.
-
Rain removal is achieved by windshield wipers and chemical rain repellent.
-
Thermal ice protection prevents engine inlet icing.
-
Electrical anti-ice systems protect static ports and sensors.
-
Ice detectors provide warning of ice accumulation to crew.
-
Integrated system combines pneumatic, thermal, and electrical anti-ice methods.